Role of AI and IP Trends in Robotic Surgery Devices
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) has significantly strengthened robotic surgery, enhancing precision, efficiency, and access to specialized care. Initially, AI applications in robotic surgery focused on automating tasks like suturing to reduce surgeon workload. Today, AI-powered systems incorporate tools like image recognition, motion control, and haptic feedback, allowing for real-time analysis and refined precision during operations. While the advantages include reduced fatigue for surgeons and improved patient safety, challenges such as high costs, data quality, and ethical concerns hinder widespread adoption. Future advancements could bring even greater autonomy, personalized approaches, and sophisticated training through virtual reality. However, thoughtful, responsible adoption is essential to unlocking the full potential of AI-driven robotic surgery in transforming healthcare.
Exploring AI’s Impact on Healthcare and Advancements in Robotic Surgery
AI is transforming healthcare by enhancing diagnostics, treatment, and patient engagement. In medical imaging, AI-powered tools analyse X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans with high precision, often detecting diseases earlier and more accurately than human interpretation. Predictive analytics, fueled by AI, analyzes patient data to anticipate health risks and potential complications, allowing for proactive and personalized care. In the surgical arena, AI-assisted robotics improve precision and control, making minimally invasive procedures more accessible and effective, reducing patient recovery times, and improving overall outcomes. Additionally, AI speeds up drug discovery by identifying promising compounds, significantly cutting down the time and costs associated with traditional research.
Beyond diagnostics and treatment, AI also plays a crucial role in supporting patient engagement and operational efficiency. Virtual health assistants, such as AI-driven chatbots, provide patients with real-time information, assist with appointment scheduling, and send medication reminders, which fosters better adherence to treatment plans. AI also streamlines administrative tasks like billing, scheduling, and documentation, enabling healthcare providers to devote more time to direct patient care. Through these advancements, AI is helping to make healthcare more efficient, accurate, and accessible, with the potential to broaden access to quality care and improve patient outcomes worldwide.
The Future of AI Integration in Robotic Surgical Devices
In current AI-assisted surgeries, clinicians remain in control, using AI to enhance decision-making and maintain patient safety, which is more acceptable in the short term to surgeons, patients, and policymakers. However, as AI advances, it could autonomously handle more complex tasks like patient consultations, diagnostics, and even surgery, retaining a human touch through empathy-driven interactions. Future surgical robots may reach levels of autonomy that enable deployment in remote areas and conflict zones, potentially setting a new standard in healthcare and reducing the need for human supervision.
This progression towards artificial general intelligence (AGI) raises significant ethical and legal questions, particularly regarding accountability if autonomous systems cause harm. While robots may hold accountability or liability, assigning culpability is complex, as they lack civil liberties; responsibility may ultimately rest with manufacturers or operators. Additional ethical challenges include defining standards for AI-to-AI interactions, protecting AI rights, training robots for ethical decision-making, and determining performance certification for autonomous systems. As AI in healthcare grows, it is essential to develop robust, adaptable regulatory frameworks with input from experts across fields to ensure safe, responsible integration.
Annual Overview of Patent Publications
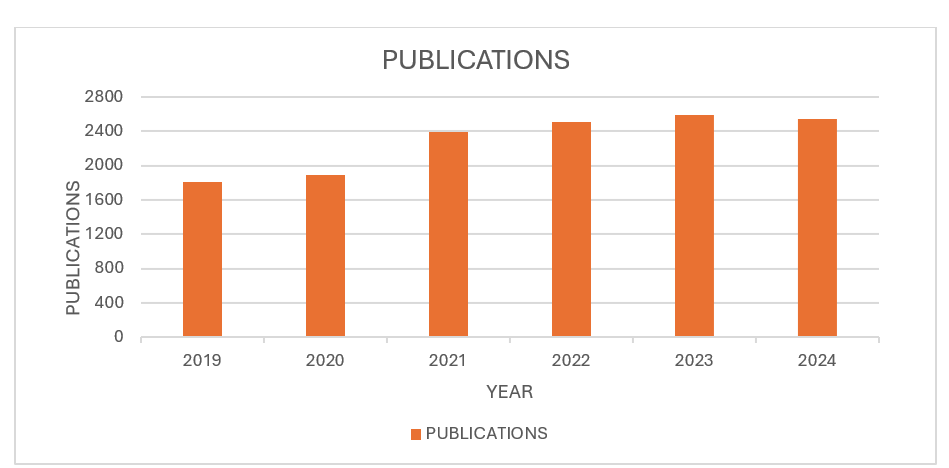
Source: Derwent Innovation
Over the past five years, there has been a consistent increase in the volume of publications, indicating a growing interest and significant advancements in the field. In 2019, 1,806 publications were recorded, followed by an increase to 1,895 in 2020. This upward trend continued in 2021, with 2,389 publications, and further rose to 2,510 in 2022, peaking at 2,592 in 2023. In 2024, while there has been a slight decline to 2,542 publications, it is important to note that the year has not yet concluded. Cumulatively, these years represent a total of 10,550 publications, underscoring a sustained and strong commitment to research and development in the field.
Leading Countries by Patent Applications
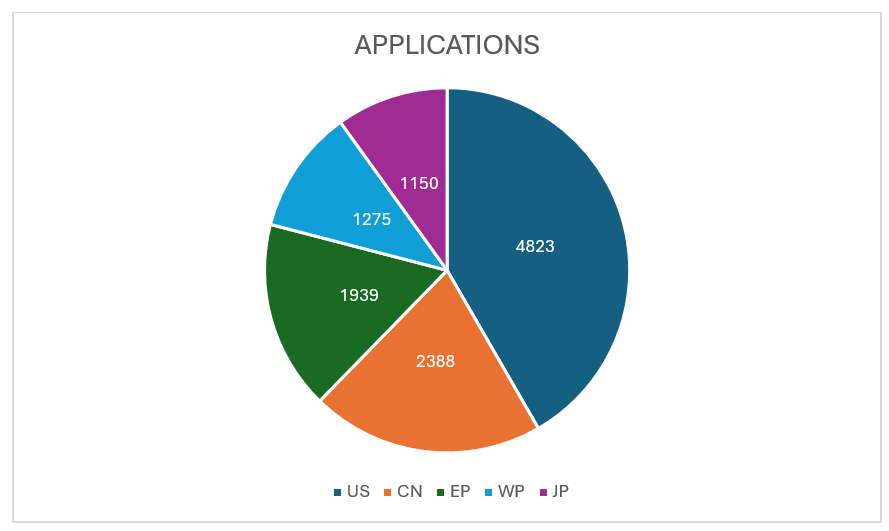
Source: Derwent Innovation
The distribution of applications across leading countries highlights the United States as the top contributor, with a total of 4,823 applications. China follows with 2,388 applications, indicating strong engagement in the field. The European Patent Office (EP) has recorded 1,939 applications, while the World Intellectual Property Organization (WP) accounts for 1,275. Japan rounds out the list with 1,150 applications. This data underscores the active participation of these countries in driving innovation and advancing research and development on a global scale.
Leading Patent Holders
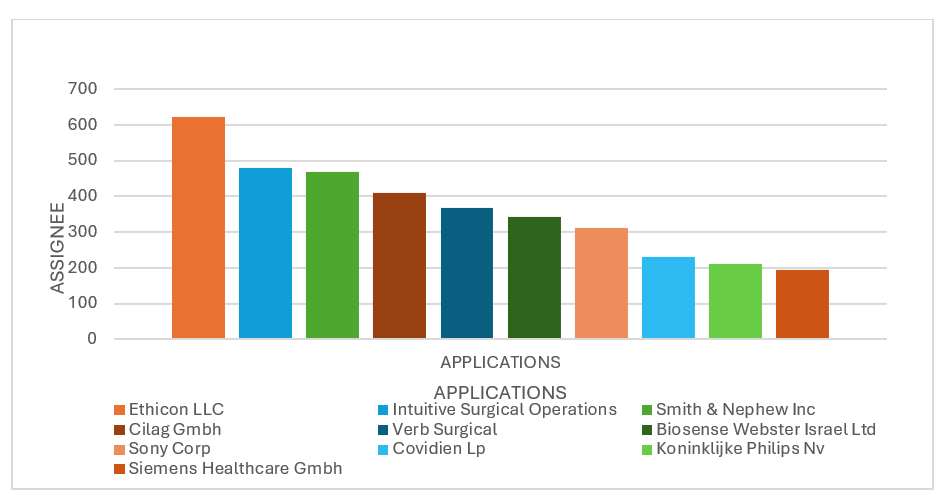
Source: Derwent Innovation
Among the top assignees in the field, Ethicon LLC leads with 623 applications, followed by Intuitive Surgical Operations with 479 applications, and Smith & Nephew Inc. with 469. Cilag GmbH has contributed 411 applications, while Verb Surgical follows closely with 368. Biosense Webster Israel Ltd has submitted 344 applications, and Sony Corp has 311. Covidien LP, Koninklijke Philips NV, and Siemens Healthcare GmbH also rank among the top contributors with 232, 212, and 194 applications, respectively. This data reflects the strong innovation efforts of these organizations, each actively advancing research and development in the field.
Five-Year Summary of Patent Filings by Major Patent Offices
Over the last five years, the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) has seen the highest number of filings, with a total of 4,823 applications, demonstrating strong innovation activity in the US. China follows with 2,388 filings, while the European Patent Office (EPO) recorded 1,939 applications. Japan Patent Office (JPO) accounted for 1,150. South Korea has 541 filings, Australia 319, Canada 222, Germany 182, and India 167. This distribution reflects a global engagement in research and development, with notable contributions across major patent offices worldwide.
Source: Derwent Innovation
Famous lawsuits in the AI in robotic surgery
Review of J&J Subsidiary’s Renewed Challenge to Intuitive’ s Surgical Robot Patent
The Federal Circuit’s decision to revive Auris Health’s challenge against Intuitive Surgical Operations’ patent could reshape competitive dynamics in the surgical robotics industry. The court’s ruling indicates that scepticism or resistance to robotic surgery at the time of invention should not alone protect a patent from an “obviousness” challenge. Auris’ argument hinges on the notion that prior inventions should have been considered as combining into an obvious solution, impacting patent robustness in this sector. This ruling directs the U.S. Patent Trial and Appeal Board (PTAB) to reassess the patent, possibly setting a precedent that could influence future cases involving high-tech medical device patents.
Benefits and Opportunities
Encouraging innovation and competition, challenges to patents based on prior technologies, like Auris’s case, promote a more open landscape in robotic surgery by limiting overly broad patents and enabling companies to focus on creating unique, advanced technologies. Additionally, the court’s stance on “industry scepticism” brings important clarity for the legal community, setting boundaries on using scepticism as a defence in patent cases, which may simplify future disputes in rapidly advancing fields like AI and robotics. For healthcare providers, this increased competition could result in a wider range of robotic surgery tools and systems, leading to more options, potentially lower costs, and improved patient outcomes by enhancing access to advanced surgical technologies.
Challenges and Drawbacks
The potential invalidation of patents that limit competition in the surgical robotics field could result in increased market fragmentation, with multiple companies offering similar technologies, which may lead to intellectual property disputes and difficulties in maintaining a distinct market presence. Financially, patent protections offer companies a crucial edge in recouping R&D investments, so if Intuitive loses exclusivity over specific technologies, it could experience significant revenue impacts. This, in turn, might make investors wary of backing companies with weaker patent protections in competitive, innovation-heavy industries.
Additionally, the court’s mixed stance on “industry scepticism” introduces legal ambiguity; while the majority suggests that scepticism alone does not prevent a finding of obviousness, the dissent raises concerns about establishing a rigid rule against considering it. This could lead to varied interpretations in lower courts, potentially causing inconsistencies in how patents are evaluated across the legal system.
Stakeholder Implications
A favourable outcome for Auris Health would enhance its competitive position against Intuitive Surgical, strengthening Johnson & Johnson’s foothold in the surgical robotics market by potentially removing patent restrictions, thus enabling Auris to innovate and expand more freely. Conversely, for Intuitive Surgical, a negative ruling could mean a loss of competitive edge, as patent protection for this specific technology might be removed, impacting revenues from its bronchoscopy tools and necessitating a stronger focus on developing unique, advanced technologies that are more challenging to dispute on grounds of obviousness. Healthcare providers, including hospitals and surgical centres, stand to benefit from the increased competition, which could lead to more affordable and varied robotic solutions, ultimately enhancing patient care options and surgical outcomes.
However, they may face challenges in choosing between similar systems, requiring careful consideration of factors like efficacy, interoperability, and cost-effectiveness. On a broader scale, this case could impact other companies in the medical and tech sectors; if the patent is invalidated, it could set a precedent that makes it harder to protect incremental innovations in robotics and AI, encouraging future patent filers to develop more distinct, novel applications instead of relying on broad technological claims. For legal and regulatory professionals, this case underscores the importance of establishing clear non-obviousness in patent applications, especially in advanced fields, and may drive regulatory bodies to refine patent guidelines in tech-heavy industries to balance innovation with the prevention of monopolistic practices.
Conclusion
The evolution of AI in robotic surgical devices signals a transformative future for healthcare, with the potential to redefine precision, accessibility, and efficiency in the field. As seen in the renewed patent challenges between industry leaders like Auris Health and Intuitive Surgical, innovation continues to push boundaries, highlighting both opportunities and complexities. While advancements in AI-integrated robotic surgery offer promising benefits, such as enhanced patient care and reduced costs, they also bring forth challenges around intellectual property rights, regulatory standards, and ethical considerations.
Moving forward, balanced legal frameworks and collaborative efforts among healthcare providers, innovators, and policymakers will be essential to navigate these challenges responsibly. By fostering a landscape that promotes fair competition, robust patent protections, and ethical oversight, stakeholders can unlock the full potential of AI-driven robotic surgery to create a more advanced, accessible, and safe healthcare environment for all.
At Legal Advantage, we specialize in supporting patent filings and guiding clients through the intricate intellectual property landscape within the field of AI in robotic surgery. Our dedicated team is committed to protecting innovations that are redefining surgical precision, from AI-driven diagnostic tools to advanced robotic surgical systems. Through our comprehensive consultation and strategic patent services, we empower inventors and organizations to secure their breakthroughs in robotic surgery, ensuring that their intellectual property contributes to a safer, more efficient, and technologically advanced future in healthcare.


